| Simple & fast to use | Highly specific | Consistent phenotypes |
| Validation-inclusive guarantee | Customized design using latest annotations | HPLC-purified and non-toxic |
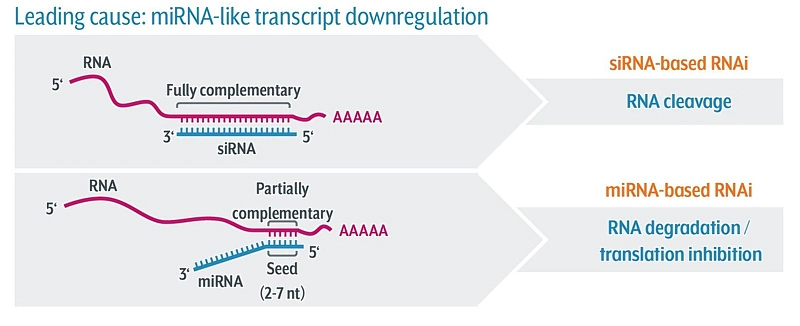
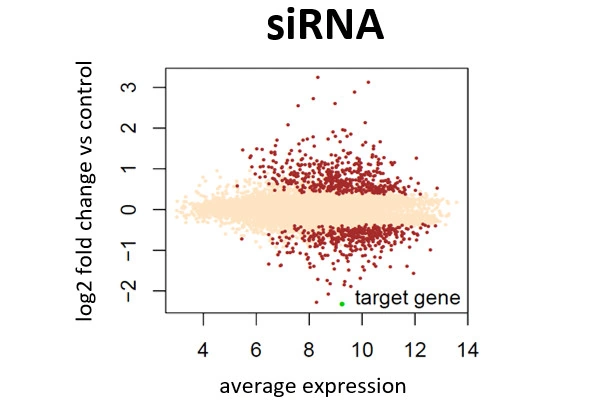
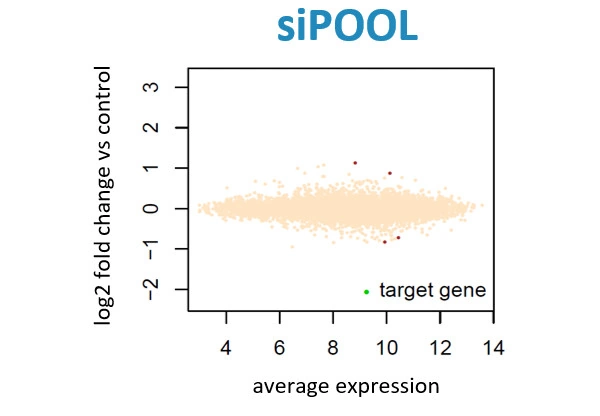
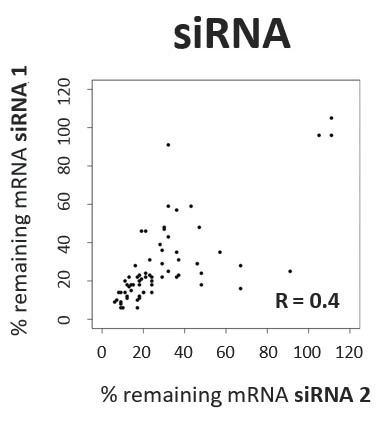
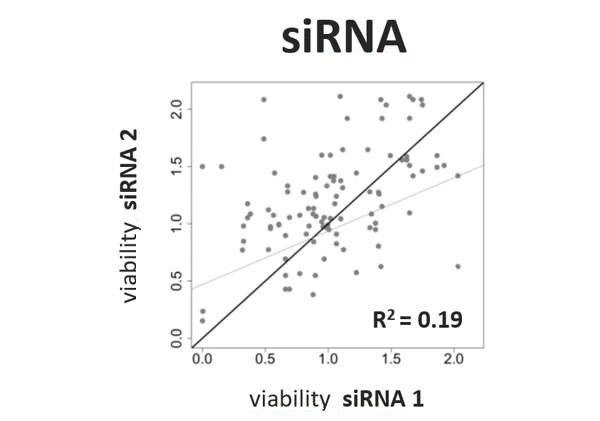
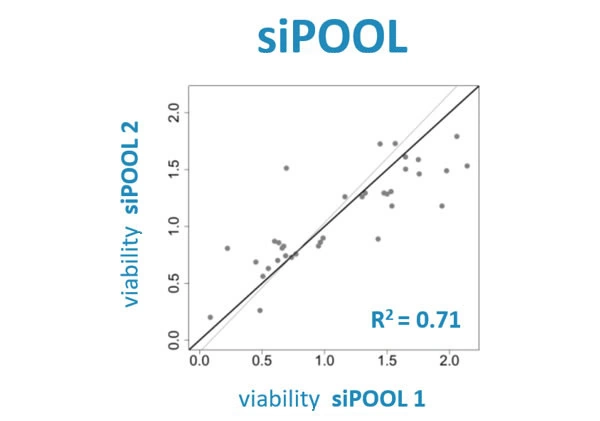
Scientists have been using RNA interference (RNAi) as a rapid and efficient tool to establish gene function. Yet the off-target effects and variable performance of short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) remain a troubling drawback, consuming precious time and resources in validation efforts.
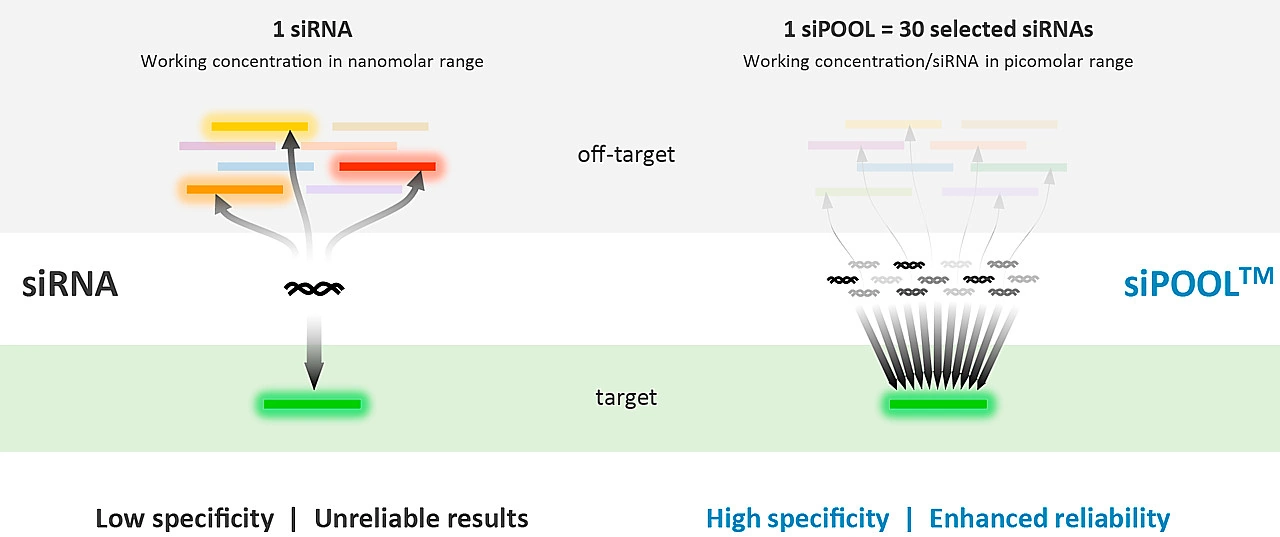
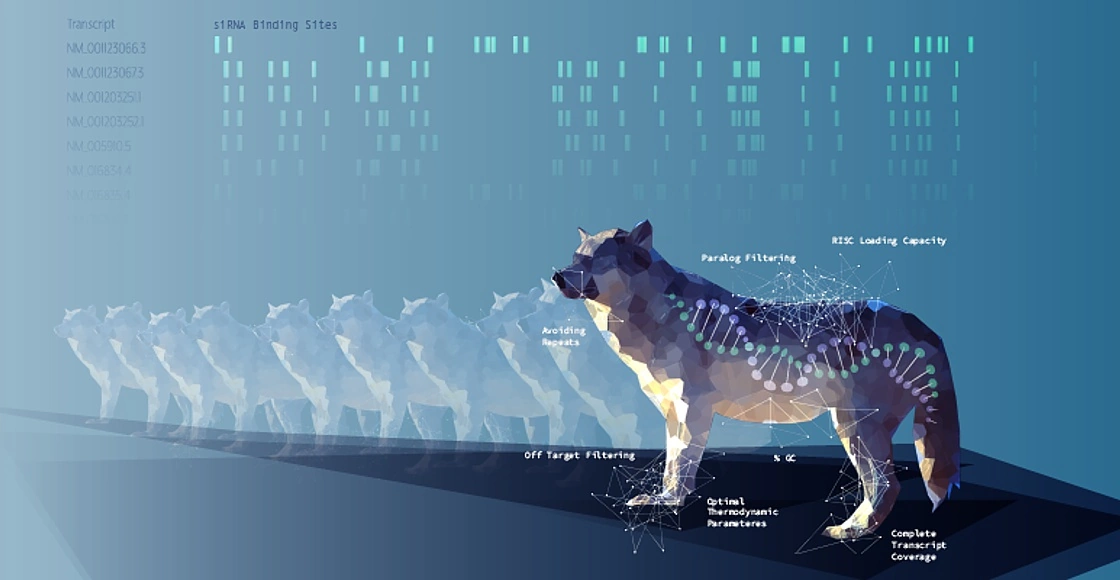
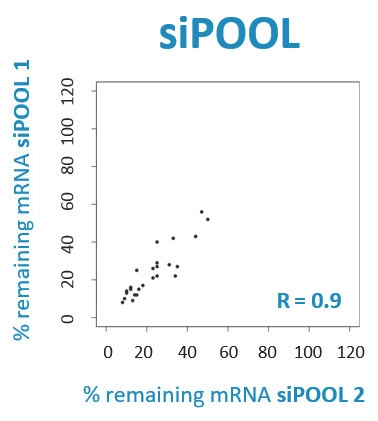
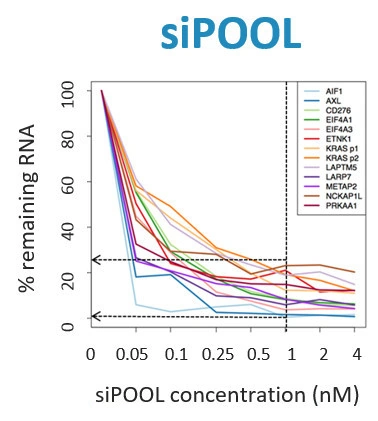
With defined siRNA sequences within the siPOOL, targeting can be optimized against specific transcript isoforms or closely related genes. Proprietary siRNA design algorithms select the most potent siRNAs based on thermodynamic properties that favour guide strand loading into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) (refer Technote 2 for more details on siPOOL design). Using latest RefSeq annotations and genome-wide paralogue filtering, siPOOLs are designed for maximum coverage of all targeted transcripts with high specificity.
Dessauges et al. (2022) Optogenetic actuator – ERK biosensor circuits identify MAPK network nodes that shape ERK dynamics Molecular Systems Biology
Kerstin Dörner et al. (2022) Genome-wide RNAi screen identifies novel players in human 60S subunit biogenesis including key enzymes of polyamine metabolism Nucleic Acids Research
Falke et al. (2022) Knockdown of the stem cell marker Musashi-1 inhibits endometrial cancer growth and sensitizes cells to radiation Stem Cell Research & Therapy
Lechner et al. (2022) Target deconvolution of HDAC pharmacopoeia reveals MBLAC2 as common off-target Nature Chemical Biology
Read more publications on siPOOLs
Please use the form below to request for a quote or ask for more information about siPOOLs.